Pregnancy is a critical period for a woman’s health. Consuming essential pregnancy nutrition is quite challenging and it is necessary for the development and growth of the fetus, as well as for the mother’s health.
Lack of proper nutrition during pregnancy can lead to severe complications, including low birth weight, premature delivery, and even birth defects.
In this blog, we will explore the essential pregnancy nutrition, including macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as micronutrients like folic acid, iron, calcium, and vitamin D.
We will also discuss the importance of hydration during pregnancy and the potential risks associated with nutrient deficiencies.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy do you need essential pregnancy nutrition?
During pregnancy, the body goes through various changes, and there is an increased demand for nutrients to support the growing fetus and prepare the mother’s body for childbirth and lactation.
Here are some of the reasons why you need essential pregnancy nutrition

- To support fetal growth and development
- To prevent birth defects
- To maintain maternal health
- To reduce the risk of pregnancy complications
- To support lactation and breastfeeding
What are the essential pregnancy nutrition?
It’s crucial to have a balanced diet during pregnancy that contains a range of vital nutrients, including both macronutrients (which the body requires in greater proportions) and micronutrients (which the body needs in smaller amounts).
During pregnancy, the following nutrients are necessary:

Macronutrients
Protein is important for the growth and development of the fetus, and for the production of new cells and tissues in the mother’s body. Good sources of protein include lean meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, nuts, and seeds.

Carbohydrate is an important source of energy for both the mother and the fetus. Complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are a better choice than simple carbohydrates such as refined sugar.

Fats are important for the development of the fetal brain and nervous system. Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty seafood, and avocados are all excellent sources of healthful fats.
Micronutrients
Folic acid helps in the formation of the fetal neural tube, which develops into the brain and spinal cord. Good sources of folic acid include leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, and fortified foods such as bread and cereal.
Also read, the importance of folic acid in pregnancy
Iron is important for the formation of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the fetus. Lean red meat, chicken, fish, beans, and fortified grains are all excellent sources of iron/
Calcium is essential for the development of the fetal skeleton and teeth. Dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods like orange juice and tofu are all excellent sources of calcium.

Vitamin D is important for the absorption of calcium and the development of the fetal skeleton. Good sources of vitamin D include fatty fish and fortified milk and cereal.
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for the development of the fetal brain and eyes. Omega-3 fatty acids can be found in fatty fish, flaxseed, and walnuts.

Vitamin C is important for the development of fetal cartilage, bones, and teeth. Good sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, and broccoli.
Zinc is an important micronutrient needed during pregnancy to support fetal growth and development, maintain maternal health, and reduce the risk of preterm birth.
Hydration – Importance of water intake during pregnancy
Water consumption is crucial during pregnancy since it supports both the mother’s and the fetus’s health.
In order to control body temperature, deliver nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, and remove waste items from the body, proper hydration is necessary. Also, it aids in avoiding typical pregnancy-related issues like urinary tract infections, hemorrhoids, and constipation.
Dehydration during pregnancy, which can result in issues like premature labor, low amniotic fluid levels, and decreased breast milk production, can be brought on by inadequate water intake.

At least 8 to 10 glasses of water should be consumed each day when pregnant, however, this amount may change depending on the demands and circumstances of the individual.
Consequently, pregnant women should deliberately make an effort to drink enough water throughout the day to support a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
What are the potential risks of nutrient deficiencies?
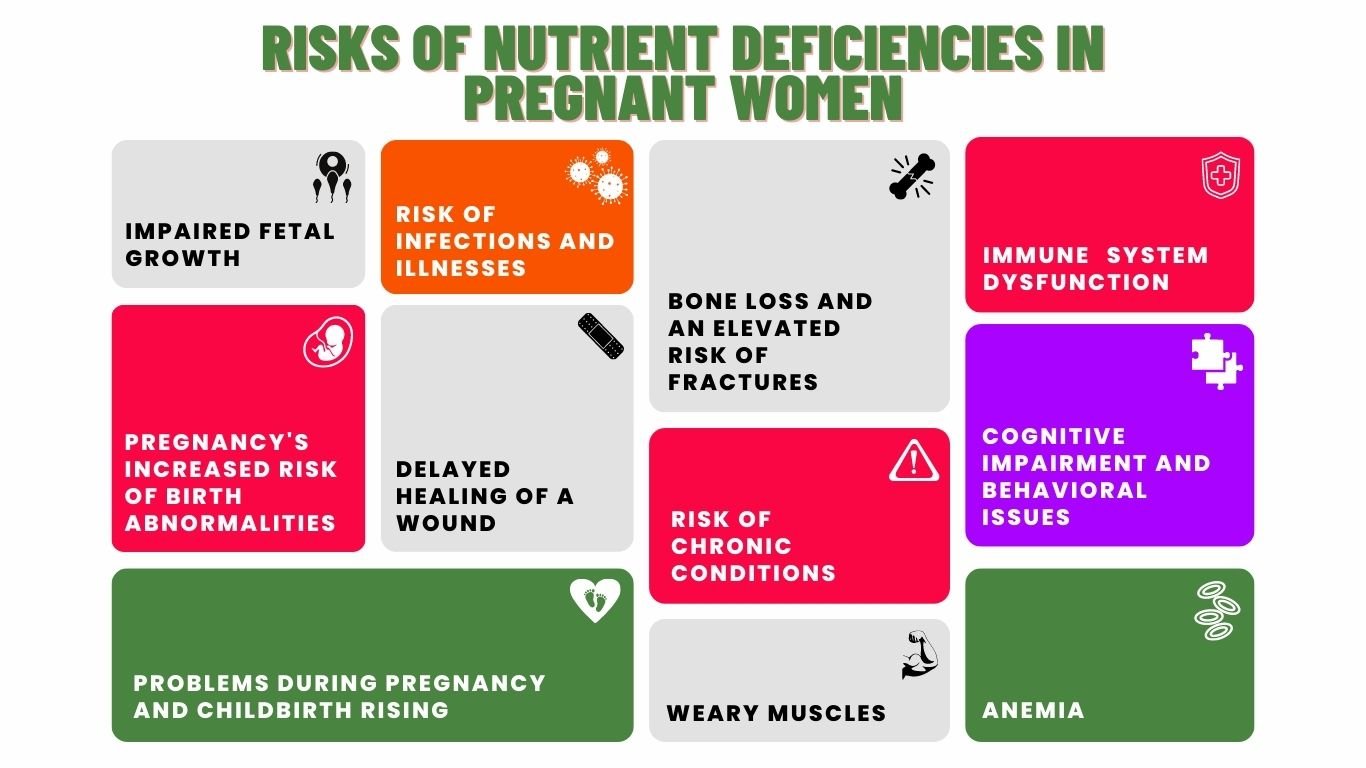
Here are some potential risks of nutrient deficiencies:
- Impaired growth and development
- Increased risk of infections and illnesses
- Anemia
- Delayed healing of a wound
- Bone loss and an elevated risk of fractures
- Cognitive impairment and behavioral issues
- Pregnancy’s increased risk of birth abnormalities
- Risk of problems during pregnancy and childbirth rising
- Risk of chronic conditions like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease
- Immune system dysfunction
- Weakness and weary muscles
Conclusion
The body’s demand for nutrients during pregnancy increases to support the growth and development of the baby, as well as to maintain the mother’s health.
One of the ways to ensure that pregnant women are getting adequate nutrition is through regular prenatal care, which includes monitoring their diet and nutritional status.
Jammi Scans, a leading pregnancy scan center, offers a range of scan services that can help pregnant women monitor their health and the health of their babies. contact us now
Chennai Women’s Clinic is now Jammi Scans
Deepthi
Dr. Deepthi Jammi (Director, Jammi Scans) is a qualified OB/GYN and Post-Doc in Maternal Fetal Medicine. As a pregnancy ultrasound expert, she is passionate about healthy pregnancies and works towards spreading awareness on the latest diagnostic options available for parents to choose from. Dr.Deepthi has received gold medals and awards in Fetal Medicine at international and national conferences, and has appeared in numerous prestigious regional magazines and TV interviews.




