Table of Contents
What is NT Scan?
The nuchal translucency ultrasound or NT Scan is a routine prenatal test that helps your doctor determine your baby’s chromosomal disorder risk. In this blog let us discuss the NT scan report sample in detail.
Understanding the Nt scan report is always essential for expectant parents to make any important decisions regarding their pregnancy.
The main objective of the NT screening determines the likelihood that your unborn child will have specific chromosomal abnormalities (Trisomy 13, 18, and 21).
When is the Nuchal Translucency (NT) ultrasound is done?
An ultrasound that detects nuchal translucency, is usually carried out between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation.
What does Nuchal Translucency mean?
The fluid at the back of your baby’s head and neck, just beneath the skin, is called a nuchal translucency.
The nuchal translucency (or NT) measurement is a method for accurately determining the fluid’s thickness.
Normally, there isn’t much fluid present, which results in a thin NT measurement.
Under specific circumstances, the fluid content can rise, resulting in a thicker NT measurement.
Several chromosome abnormalities, such as trisomy 13, 18, and 21, and some structural issues are linked to increased NT measurements (for example, heart abnormalities).
Although a higher NT measurement does raise the risk, it does not always indicate that the baby has a problem.

Your gynecologist might ask you to come back for additional pictures later in the day if your baby is not cooperating and the NT cannot be measured precisely.
How is the NT test performed?
The NT scan can be performed either transabdominal or transvaginally.
In transabdominal your lower abdomen’s skin is covered with a small amount of ultrasound gel, which is then scanned by the ultrasound probe.
The gel enhances the probe’s ability to make contact with your skin.
Depending on the mother’s health condition, transvaginal scan will also be done.
Is a full bladder required for an accurate NT scan report?
Your fetal medicine specialist will typically get better images during transabdominal ultrasound if the bladder is partially filled, so it is advised that you drink water before the examination.
Please try not to empty your bladder again until after your appointment, after which you should drink two glasses of water.
A full bladder causes the bowel to move from the pelvis into the abdomen, making the uterus, cervix, and pregnancy easier to visualize.
Your bladder shouldn’t be so uncomfortably full. You should empty a small amount of urine from your bladder if it is extremely full and painful in order to feel better.
After the transabdominal ultrasound is finished and before the transvaginal ultrasound starts, you will be able to urinate.
Which is best NT scan with or without food for a better scan report?
There is no need to keep your stomach empty; instead, eat a light meal.
How accurate is the NT scan report?
Approximately eight out of every ten infants with Down syndrome are detected by the nuchal scan alone.
For an NT scan, there are 5% false-positive results.
Accordingly, one woman out of every 20 receives a high-chance calculation that is incorrect.
A blood test and an NT scan together produce a more precise result.
The free beta-hCG hormone and the PAPP-A protein are both detected in the blood test.
Down syndrome babies typically have low PAPP-A levels and high hCG levels.
Nine out of ten babies are detected when the NT scan is combined with this blood test. This is often referred to as a combined test.
What exactly is the fetal nasal bone?
The fetal nasal bone is used in the assessment of aneuploidy risks during first-trimester screening at Advanced Women’s Imaging, which is accredited.
The use of the fetal nasal bone can have a significant impact on the management and outcomes of your pregnancy.
Using the fetal nasal bone could make or break your pregnancy. It could mean the difference between detecting a chromosome problem and missing it. It could mean the difference between having or not having invasive prenatal diagnostic testing (CVS or amniocentesis).

The fetal nasal bone is used to increase the precision of trisomy 21 screening. By increasing trisomy 21 detection from 90% to 93%, it will find more cases of trisomy 21.
NT Scan Report Sample
The NT test report is a compilation of basic details like maternal weight, gestation period, and gravida (refers to the no of pregnancies the mother has had)
The report will also draw inferences from other intricate details like Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Hypertension.
However, the findings will primarily focus on Fetal Heart Activity, Fetal Heart Rate, Crown-rump Length (CRL), Nuchal Translucency (NT), Biparietal Diameter (BPD), Ductus Venoscus PI, Placenta, and Amniotic Fluid.
It also has data about Chromosomal Markers, with detailed information about the Nasal Bone, Tricuspic Doppler, and Fetal Anatomy including skull and brain, spine, heart, abdominal wall, stomach, bladder/kidneys, and spontaneous limb movements too.
As an expectant mother, your top concerns in this report should be fetal heart rate, neck thickness (NT), nasal bone, and blood flow
NT scan report sample when baby is normal
For a healthy baby, the normal NT scan measurements should be between 45mm (1.8in) and 84mm in size for an NT of less than 3.5mm to be considered normal (3.3in).
A newborn with an NT of 1.3mm falls into the acceptable range.
The infant’s NT value of 2.9 mm is also within the acceptable range.
The possibility of Down’s syndrome and other chromosomal disorders rises along with the NT.
A baby with an NT of 6mm is more likely to have Down’s syndrome than other chromosomal and cardiovascular disorders. It’s unusual for babies to have this much fluid.
Normal NT Scan Report Sample
Page 1:
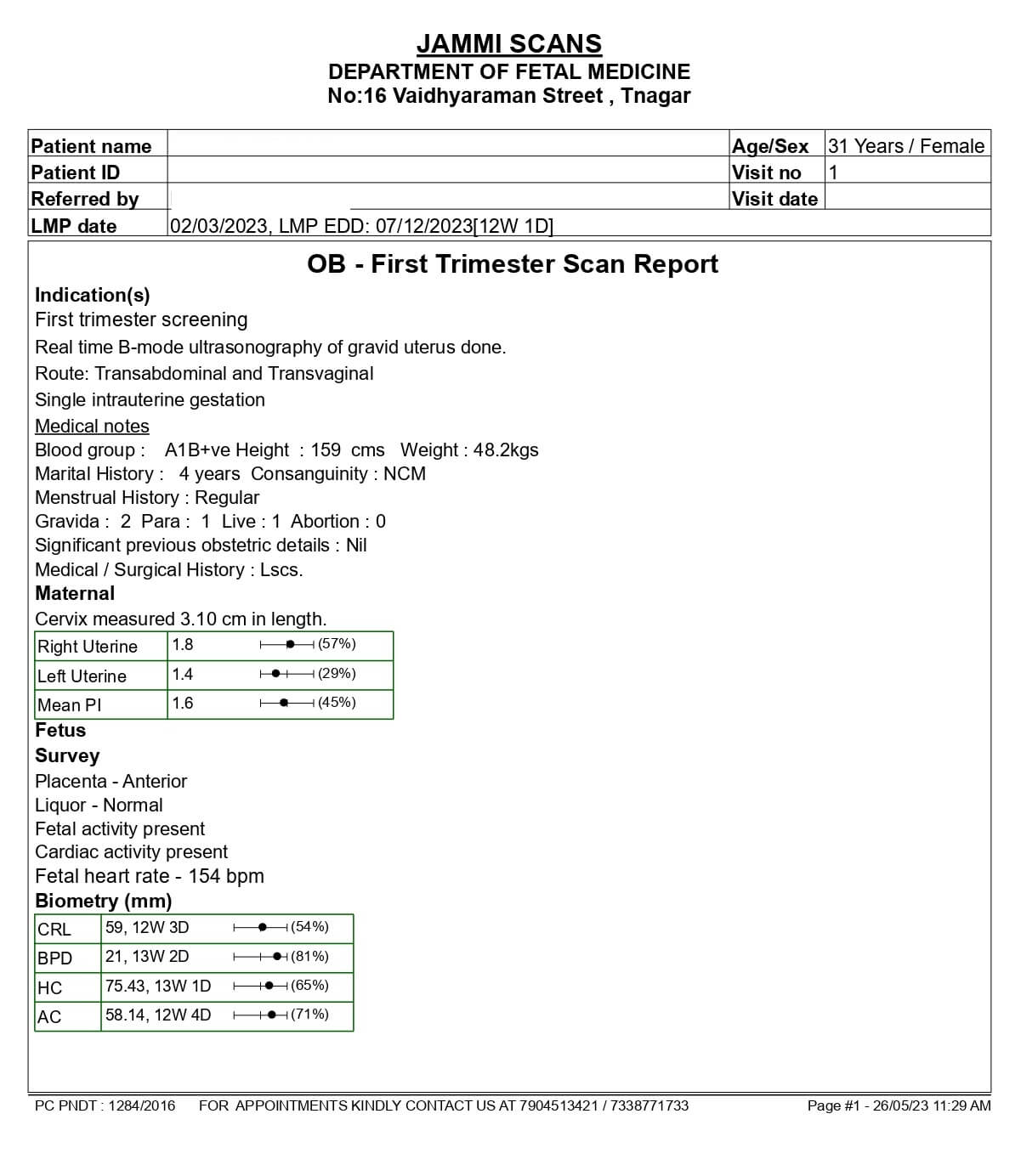
Page 2:

NT scan report sample when baby is abnormal
Any nuchal translucency that measures more than 3.5 mm on the ultrasound screen would be considered “abnormal.”
High nuchal translucency is one sign of chromosomal variation, but it is not the only one.
There have been cases of “normal” babies with “abnormal” nuchal translucency (higher nuchal fold measurement and no chromosomal abnormalities).
In fact, the likelihood of having a baby with high nuchal translucency but no significant chromosomal differences range from “70% for NT of 3.5-4.4 mm, 50% for NT of 4.5-5.4 mm, 30% for NT of 5.5-6.4 mm, and 15% for NT of 6.5 or more,” according to this study from 2011.
Abnormal NT Scan Report Sample
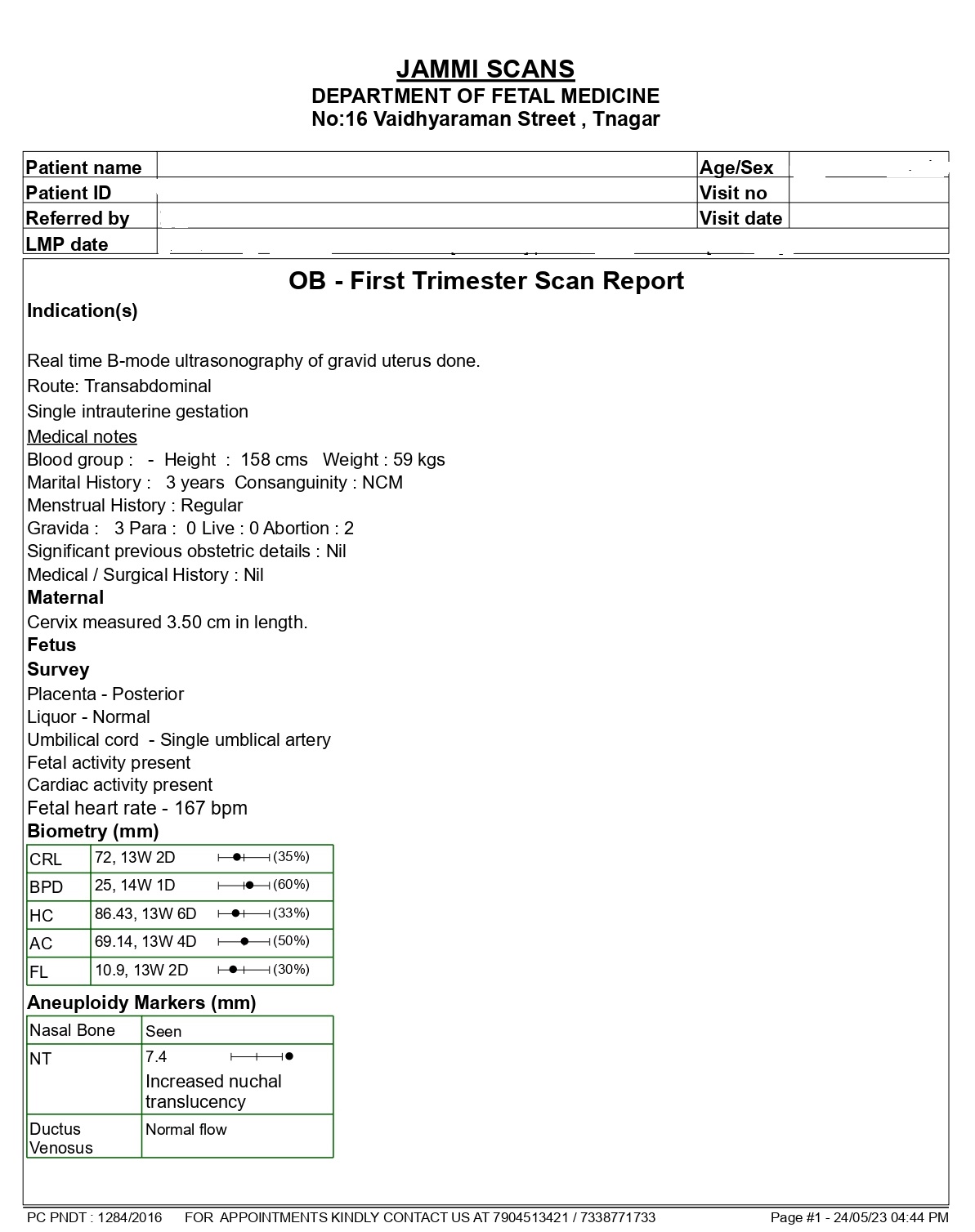

What if nuchal translucency is high in the NT scan report?
There is only a 70% chance that an “abnormal” nuchal translucency is a sign of a chromosomal difference at this stage, so if your baby has a high nuchal translucency, your doctor will probably recommend you have another test.
They might also advise getting a fetal heart scan since some chromosomal diagnoses are linked to cardiac abnormalities.
Even though it might be difficult, try not to worry if your baby does have a high nuchal translucency measurement; this doesn’t always indicate that they will have a chromosomal difference.
Is a high nuchal translucency always indicative of Down syndrome?
No, not always. A high nuchal translucency measurement can be caused by a variety of factors.
Among the causes of increased nuchal translucency are:
- Parvovirus is an infection that can cause an increase in the nuchal fold measurement of a baby.
- Birth defects of the heart (ranging from minor to major).
- Genetic syndromes that are uncommon
- High blood pressure due to venous congestion
What happens if a problem is discovered in my NT scan?
You’ll need to decide, with the help of your doctor or a fetal medicine expert, whether the results show a high enough risk that you should undergo CVS or amniocentesis to receive a conclusive diagnosis.
You must balance your desire to learn about your unborn child’s condition with the slight possibility that diagnostic testing could result in a miscarriage when making your choice.
If you choose not to have diagnostic testing, you can still learn more about your unborn child’s health and development by having a detailed ultrasound between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, as well as the quad screen, a blood test that is available to all pregnant women starting at 10 weeks of pregnancy.
The “soft markers” of chromosome disorders that this ultrasound can identify include short limbs, a bright dot in the heart, a bright bowel, and specific kidney issues. Additionally, it can search for structural flaws like spina bifida.
Additional benefits of the NT scan?
An ultrasound at this point in the pregnancy has additional benefits.
- Verification of the child’s heartbeat
- Assessment of the pregnancy’s date
- Review your baby’s physical foundation
- Estimation of the number of babies in the womb
How to schedule a nuchal scan with Jammi Scans?
Our consultant – a fetal medicine expert, is a gynecologist and obstetrician who, upon diagnosis, may recommend a nuchal scan, at which point our staff will schedule a consultation for you.
Alternatively, you could contact us to schedule a consultation by using our online booking system. The help desk will set up a nuchal scan for you if you require one.
Chennai Women’s Clinic is now Jammi Scans


